Derivative of ln(tan(2x)) Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem We hope it will be very helpful for you and it will help you to understand the solving processDerivatives of Hyperbolic Functions The derivatives of hyperbolic functions can be easily found as these functions are defined in terms of exponential functions So, the derivatives of the hyperbolic sine and hyperbolic cosine functions are given by (sinhx)′ = ( ex −e−x 2)′ = ex e−x 2 = coshx, (coshx)′ = ( ex e−x 2)′ = exCompute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history

Example 22 Find Derivative Of Tan 2x 3 Chapter 5 Class 12
Tan 2 2x derivative
Tan 2 2x derivative- The derivative of `f(x)=tan(2x pi/2)` is `f'(x) = 2*sec^2(2x pi/2)` and at `x = 3*pi/4` the slope of the tangent is 2 Approved by eNotes Editorial Team Luca BTan^2 (xy^2 y) = 2x 2 tan (xy^2 y)sec^2 (xy^2 y)(y^2)(1) (x)2y(dy/dx) (dy/dx) = 2 tan(xy^2 y) sec^2 (xy^2 y) y^2 2xy(dy/dx) (dy/dx) = 1




Answered 6 Find The Equation Of The Tangent Bartleby
Using the chain rule, the derivative of tan (2x) is 2sec2(2x) Finally, just a note on syntax and notation tan (2x) is sometimes written in the forms below (with the derivative as per the calculation above) Just be aware that not all of the forms below are mathematically correct The Second Derivative Of tan (2x)Find the Derivative d/dx y=3tan(2x) Since is constant with respect to , the derivative of with respect to is Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that is where andJust for practice, I tried to derive d/dx (tanx) using the product rule It took me a while, because I kept getting to (1sin^2 (x))/cos^2 (x), which evaluates to sec^2 (x) tan^2 (x) Almost there, but not quite After a lot of fiddling, I got the correct result by adding cos^2 (x) to
Find the derivative of the following function f (x) = (arctan (2x))/ (tan (x))Derivative of Tangent Inverse In this tutorial we shall explore the derivative of inverse trigonometric functions and we shall prove the derivative of tangent inverse Let the function of the form be y = f ( x) = tan – 1 x By the definition of the inverse trigonometric function, y = tan – 1 x can be written as tanSpecify Method (new) Chain Rule;
Given a function , there are many ways to denote the derivative of with respect to The most common ways are and When a derivative is taken times, the notation or is used These are called higherorder derivatives Note for secondorder derivatives, the notation is often used At a point , the derivative is defined to beEngineering ToolBox SketchUp Extension Online 3D modeling!Derivative Calculator computes derivatives of a function with respect to given variable using analytical differentiation and displays a stepbystep solution It allows to draw graphs of the function and its derivatives Calculator supports derivatives up to




Differentiate Tanx Tan 2x Tan 3x Tan 4x W R T X




Differentiation Of Tanx 2 Youtube
The derivative of sin x is cos x, The derivative of cos x is −sin x (note the negative sign!) and The derivative of tan x is sec 2x Now, if u = f(x) is a function of x, then by using the chain rule, we have d ( sin u) d x = cos u d u d xDerivative of tan^2x \frac{d}{dx}\left(tan^{2}x\right) zs Related Symbolab blog posts Advanced Math Solutions – Derivative Calculator, Implicit Differentiation We've covered methods and rules to differentiate functions of the form y=f(x), where y is explicitly defined asDerivative of tan^2x \square!




Prove That Derivative Of Tan X Is Sec 2 X By First Principle
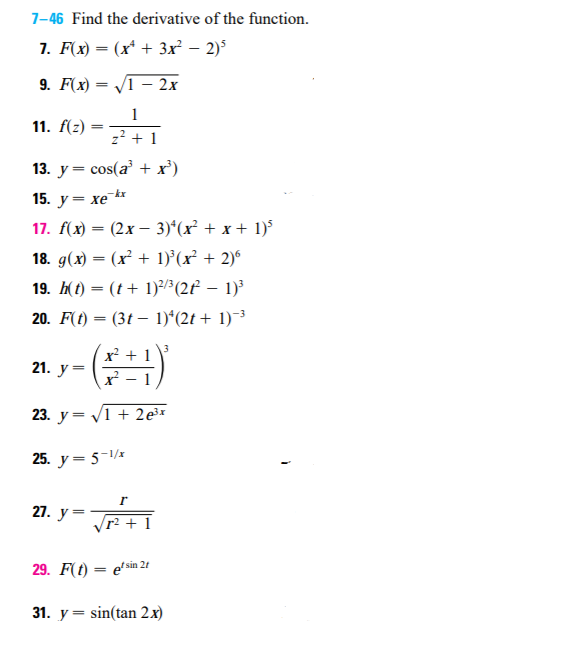



7 46 Find The Derivative Of The Function 13 Chegg Com
Approximating a Value of \(4^π\) We also assume that for \(B(x)=b^x,\, b>0\), the value \(B′(0)\) of the derivative exists In this section, we show that by making this one additional assumption, it is possible to prove that the function \(B(x)\) is differentiable everywhereAs there is no way to immediately integrate tan^2 (x) using well known trigonometric integrals and derivatives, it seems like a good idea would be writing tan^2 (x) as sec^2 (x) 1 Now, we can recognise sec^2 (x) as the derivative of tan (x) (you can prove this using the quotient rule and the identity sin^2 (x) cos^2 (x) = 1), while we getDerivative of (tan(2x))^7 Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem We hope it will be very helpful for you and it will help you to understand the solving process




Wahat Is The Derivative Of Tan Square X Brainly In




Answered 6 Find The Equation Of The Tangent Bartleby
Integral of tan^2x, solution playlist page http//wwwblackpenredpencom/math/Calculushtmltrig integrals, trigonometric integrals, integral of sin(x), integDerivative Calculator derivative of tan^2x Derivatives First Derivative;This proves from first principles that the derivative of tan x is sec^2x Approved by eNotes Editorial Team Ask a Question Ask a Question Submit Question Popular Questions See all




Find The Derivative 29 Y 8 10 Secx A Y 10 Chegg Com
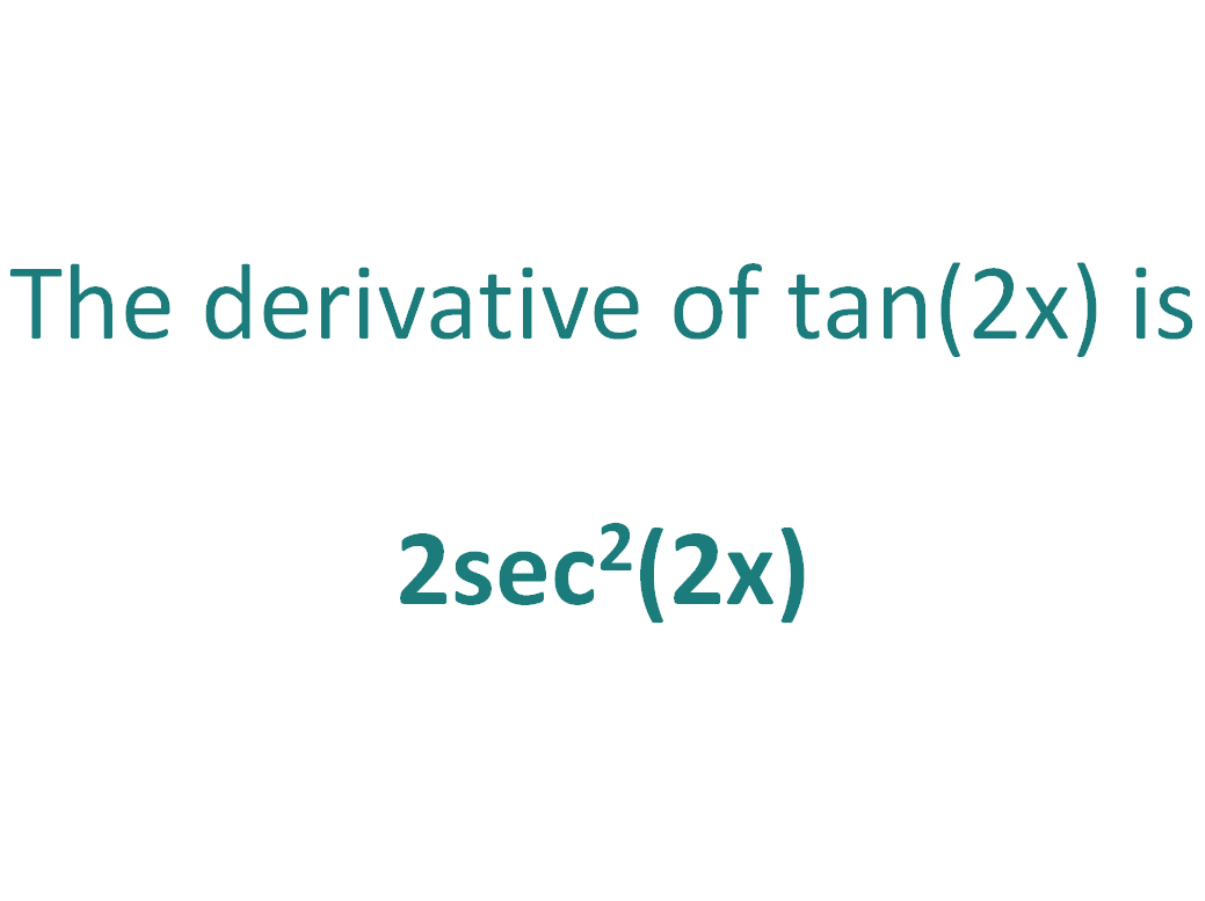



The Derivative Of Tan 2x Derivativeit
Example 22 Find the derivative of tan (2x 3) Let y = tan (2x 3) We need to find derivative of y, ie 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = (𝑑 tan〖(2𝑥3)〗)/𝑑𝑥An online derivative calculator that differentiates a given function with respect to a given variable by using analytical differentiation A useful mathematical differentiation calculator to simplify the functions Just copy and paste the below code to your webpage where youGraph of tan x and its Derivative The graphs of \( \tan(x) \) and its derivative are shown below Derivative of the Composite Function tan (u(x)) We now have a composite function which is a function (tan) of another function (u)




04 Derivative At A Value Kuta Software




Finding The Derivative Of Sec 2 X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
The derivative of tan 2x is 2 sec 2 (2x) (ie) d/dx tan 2x = 2 sec 2 (2x) Explanation We know that the derivative of tan x is sec 2 x (ie) d/dx (tan x) = sec 2 x According to the chain rule,Derivative of the Tangent Squared Function In this tutorial we shall discuss the derivative of the tangent squared function and its related examples It can be proved by the definition of differentiation We have a function of the form y = f ( x) = tan 2 x By the definition of differentiation we have d y d x = lim Δ x → 0Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes




Math 1a Ucb Spring 10




Derivative Of Tan X Sec X Tan X More
The derivative of tan (2x) is equal to two times the secant squared of two times x Using mathematical notation, the equation is written as d/dx tan (2x) = 2sec^2 (2x) The derivative of tan (2x) can be found by using the quotient rule and the chain rule 3 The instructions Use the definition of derivative to find f ′ ( x) if f ( x) = tan 2 ( x) I've been working on this problem, trying every way I can think of At first I tried this method lim h → 0 tan 2 ( x h) − tan 2Start studying Derivatives and Antiderivatives Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools




Ex 13 1 22 Lim X Pi 2 Tan 2x X Pi 2 Chapter 13 Class 11
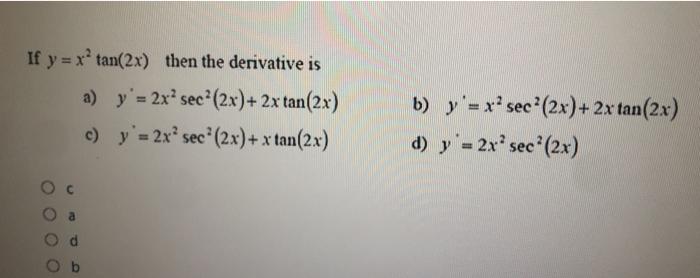



If Y X Tan 2x Then The Derivative Is A Y 2x Chegg Com
Proportionality constants are written within the image sin θ, cos θ, tan θ, where θ is the common measure of five acute angles In mathematics, the trigonometric functions (also called circular functions, angle functions or goniometric functions) are real functions which relate an angle of a rightangled triangle to ratios of two side lengths Assuming that you know the derivative rule d dx (tanx) = sec2(x) d dx (tan(2x)) will simply be sec2(2x) ⋅ d dx (2x) according to the chain rule Then d dx (tan(2x)) = 2sec2(2x)Introduction to Tan double angle formula let's look at trigonometric formulae also called as the double angle formulae having double angles Derive Double Angle Formulae for Tan 2 Theta \(Tan 2x =\frac{2tan x}{1tan^{2}x} \) let's recall the addition formula
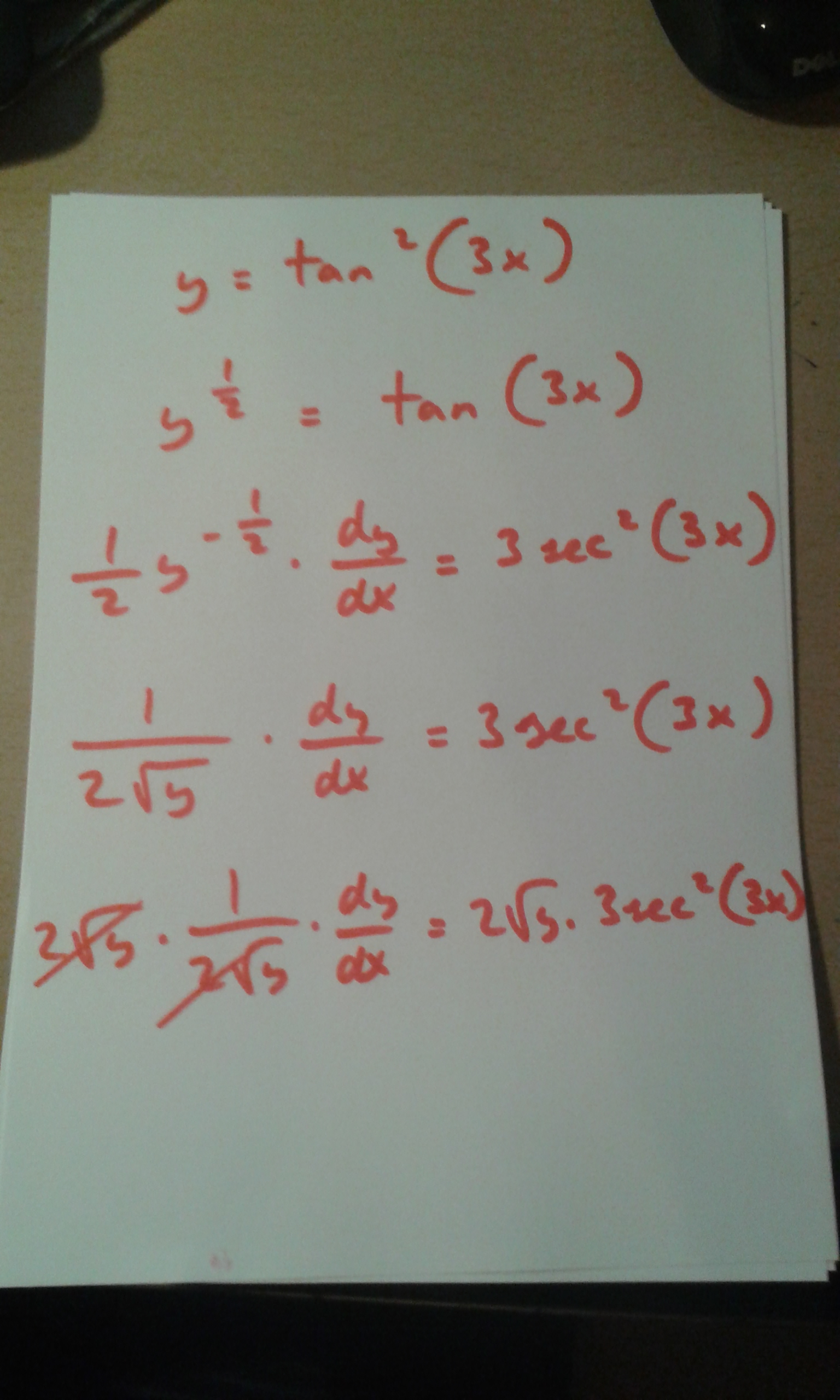



How Do You Find The Derivative Of Tan 2 3x Socratic




Example 22 Find Derivative Of Tan 2x 3 Chapter 5 Class 12
Example 16 Calculate the derivative of the function \y = \left( {2 – {x^2}} \right)\cos x 2x\sin x\ at \(x = \pi\) `=cos^2x` `3 sin^2x cos^2x` `3 sin^2x cos^2x` `cos^2x` `=0` ` ="RHS"` We have actually displayed that it is true 10 Find the derivative of y = x tan x Answer This is the product of `x` and also `tan x` So we have `d/(dx)(x tan x) =(x)(sec^2x)(tan x)(1)` `=x sec^2xtan x` See also Derivative of square root of sine x by initiallyThe differentiation of trigonometric functions is the mathematical process of finding the derivative of a trigonometric function, or its rate of change with respect to a variableFor example, the derivative of the sine function is written sin′(a) = cos(a), meaning that the rate of change of sin(x) at a particular angle x = a is given by the cosine of that angle
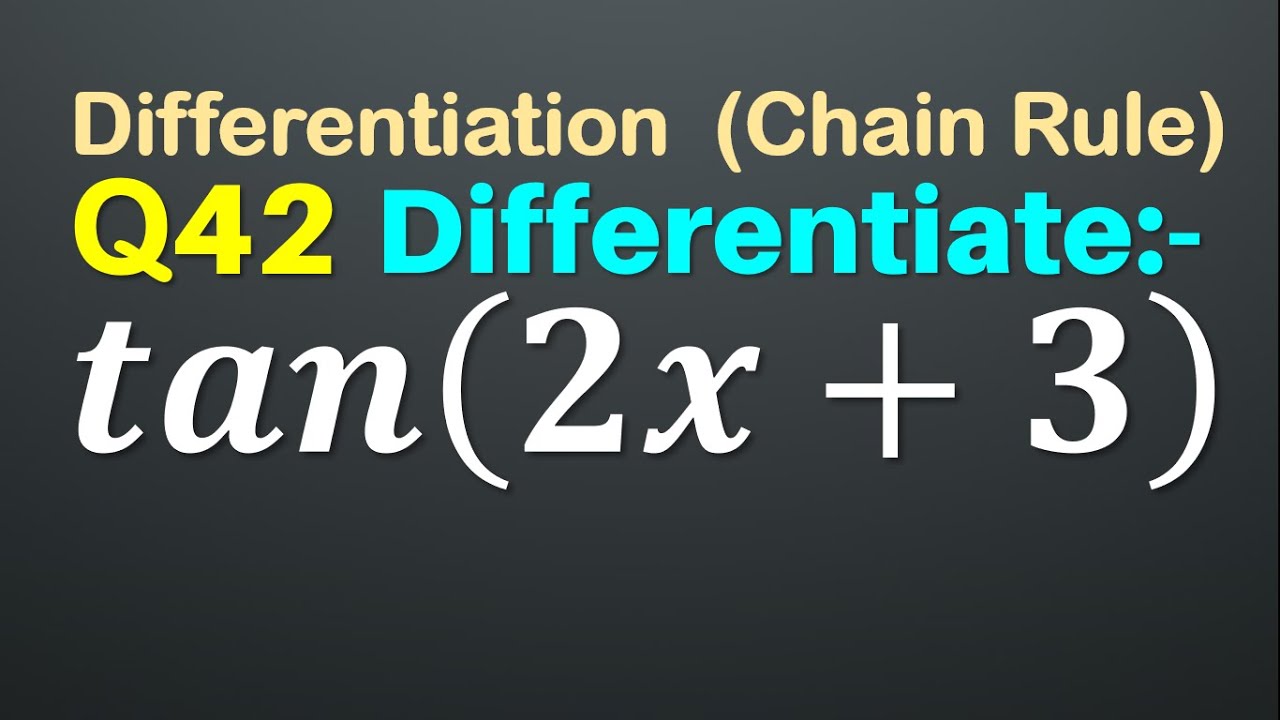



Q42 Differentiate Tan 2x 3 Derivative Of Tan 2x 3 Differentiation Of Tan 2x 3 Youtube



Www Math Purdue Edu Kyochman Ma Lesson14 Notes Implicitdifferentiation Pdf
Start studying Derivative/identities Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools The derivative of tan x is sec 2 x However, there may be more to finding derivatives of tangent In the general case, tan x is the tangent of a function of x, such as tan(tan^{2}x\right) en Related Symbolab blog posts Advanced Math Solutions – Derivative Calculator, Implicit Differentiation We've covered methods and rules to differentiate functions of
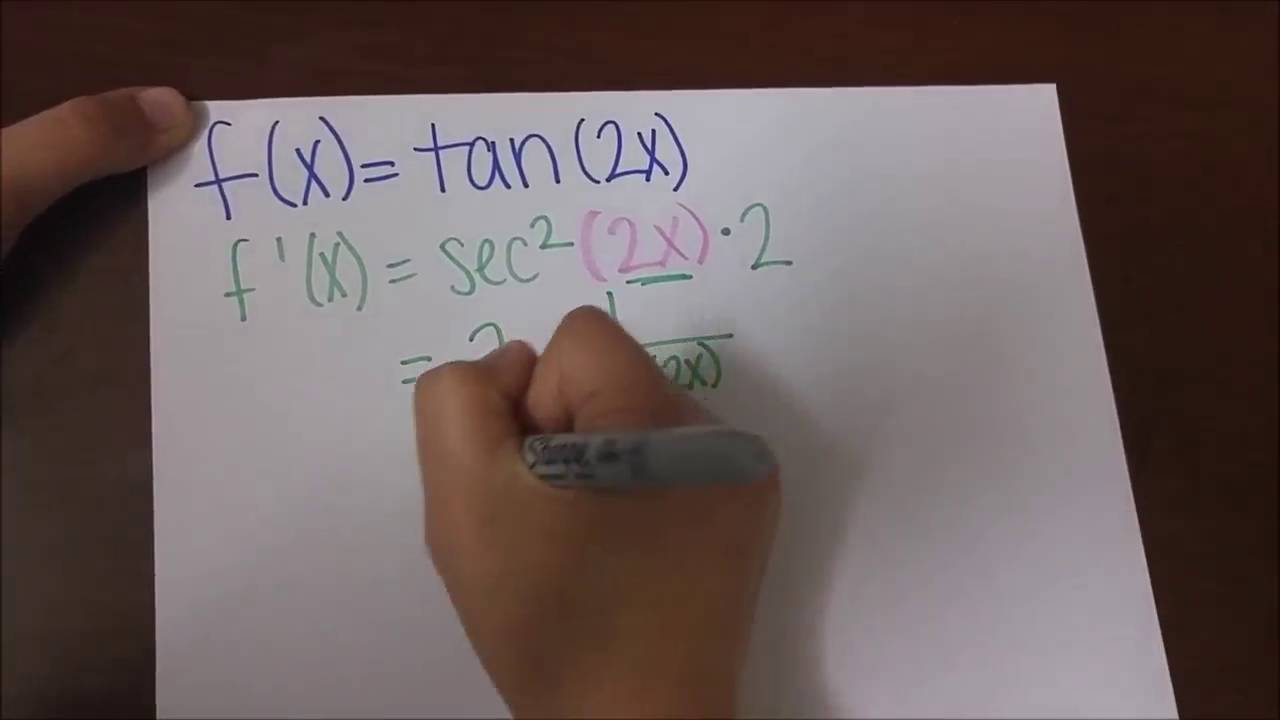



Ii F Find Derivative Of Tan 2x At X Pi 6 Youtube




What Is The Integration Of Tan 2x Solution Quora
Math\begin{align}\displaystyle y&=e^{\ln\sqrt{1\tan^2\ x}}\\y&=e^{\ln\ \sec\ x} \qquad\text{Take ln on both sides,}\\\ln \ y &=\ln\ {e^{\ln\ \sec\ x}}\\\ln\ yFind the Derivative d/dx y=tan(2xx^3) Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that is where and Tap for more steps To apply the Chain Rule, set as The derivative of with respect to is Replace all occurrences of with Differentiate Tap for more stepsDerivative of \(tanx = sec^2x \) What Is The Derivative Of tan(x)?




Larson Calculus 5 4 52 Find The Derivative Of Y E 2x Tan 2x With The Product Rule Youtube




The Derivative Of Tan X Is Sec 2 X Why Mathematics Stack Exchange
Add standard and customized parametric components like flange beams, lumbers, piping, stairs and more to your Sketchup model with the Engineering ToolBox SketchUp Extension enabled for use with the amazing, fun and free SketchUp Make and SketchUp Pro Add the Engineering ToolBox extension to your Find the derivative of \(f(x)=2\tan x −3\cot x \) Hint Use the rule for differentiating a constant multiple and the rule for differentiating a difference of two functions\(f′(x)=2\sec^2 x3\csc^2 x\) Answer \(f′(x)=2\sec^2 x3\csc^2 x\) The derivative of the former is $\frac{1}{1x^2}$, and the derivative of $\tan(x)$ is $\sec^2(x)$ Share Cite Follow answered Mar 25 '19 at 2147 Dave Dave 123k 1 1 gold badge 15 15 silver badges 36 36 bronze badges $\endgroup$ 3
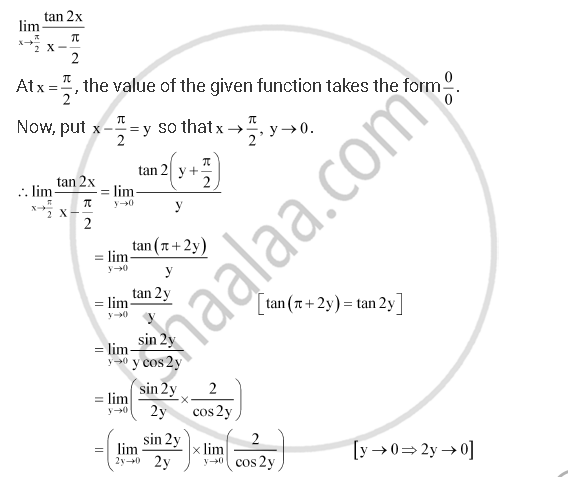



Evaluate The Given Limit Lim X Pi 2 Tan 2x X Pi 2 Mathematics Shaalaa Com
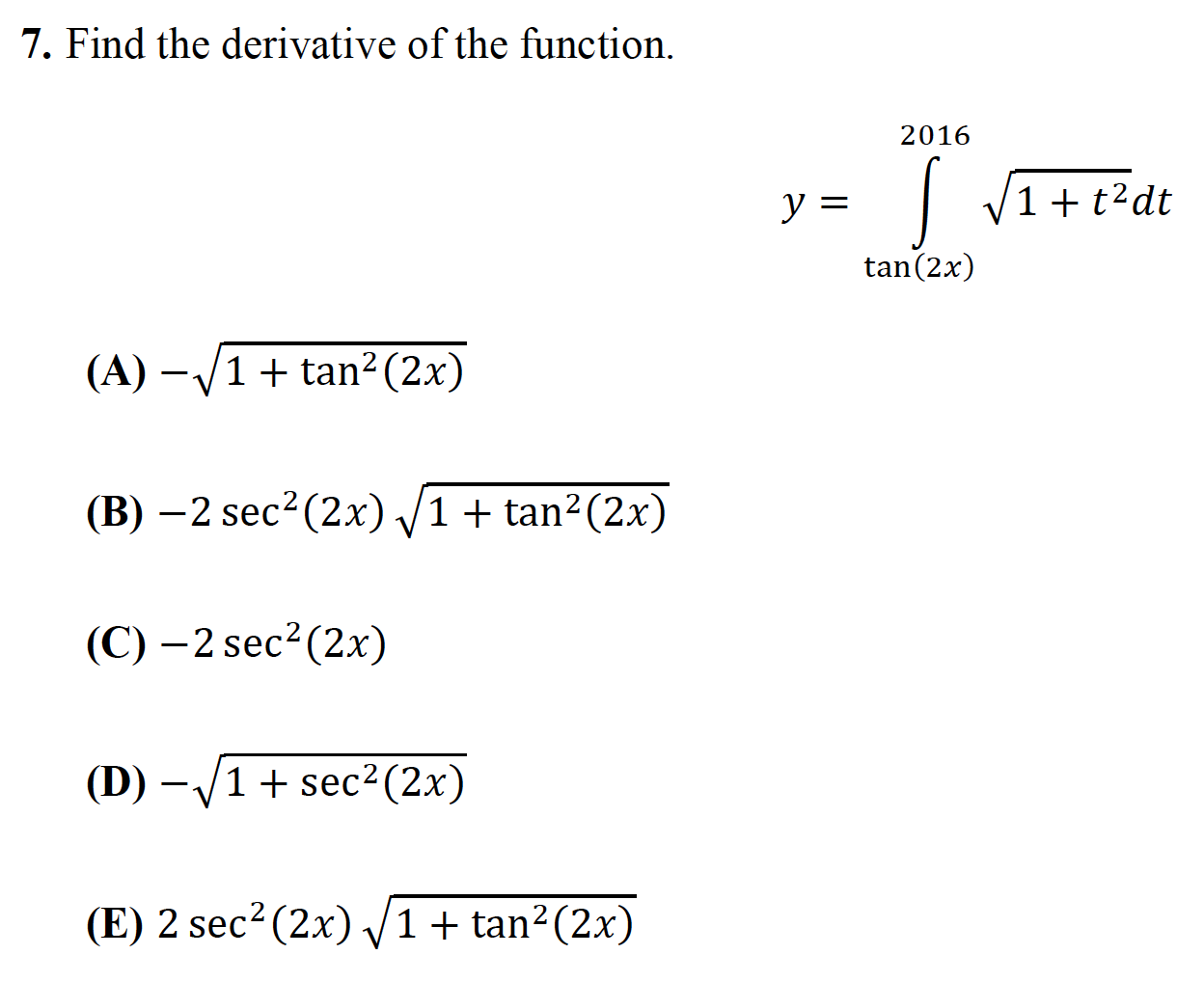



7 Find The Derivative Of The Function 16 Y 11 Chegg Com
The tangent line is the best linear approximation of the function near that input value For this reason, the derivative is often described as the "instantaneous rate of change", the ratio of the instantaneous change in the dependent variable to that of the independent variable The derivative of tan x The derivative of tan x is sec 2 x\( \frac{d}{dx} {tanx} = \frac{d}{dx} \frac{sinx}{cosx}\) we know that \( tanx =\frac{sinx}{cosx The Second Derivative Of tan^2x To calculate the second derivative of a function, differentiate the first derivative From above, we found that the first derivative of tan^2x = 2tan (x)sec 2 (x) So to find the second derivative of tan^2x, we need to differentiate 2tan (x)sec 2 (x)



3



J8htccqrkvhoim
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsThe inverse tangent — known as arctangent or shorthand as arctan, is usually notated as tan1 (some function) To differentiate it quickly, we have two options 1) Use the simple derivative rule 2) Derive the derivative rule, and then apply the rule In this lesson, we show the derivative rule for tan1 (u) and tan1 (x) There are four




Question 1 Integrate The Following Function Sec 2x Chegg Com




Find Derivative Of Xsin2x 5 X K X Tan 2x 3 Q 13 X Sin 2x 5x Kx Tan2x3 Maths Limits And Derivatives Meritnation Com




Differentiate The Following From First Principle Tan2x Youtube




Differentiation Of Tan 2 X And X 3 X 4 Youtube
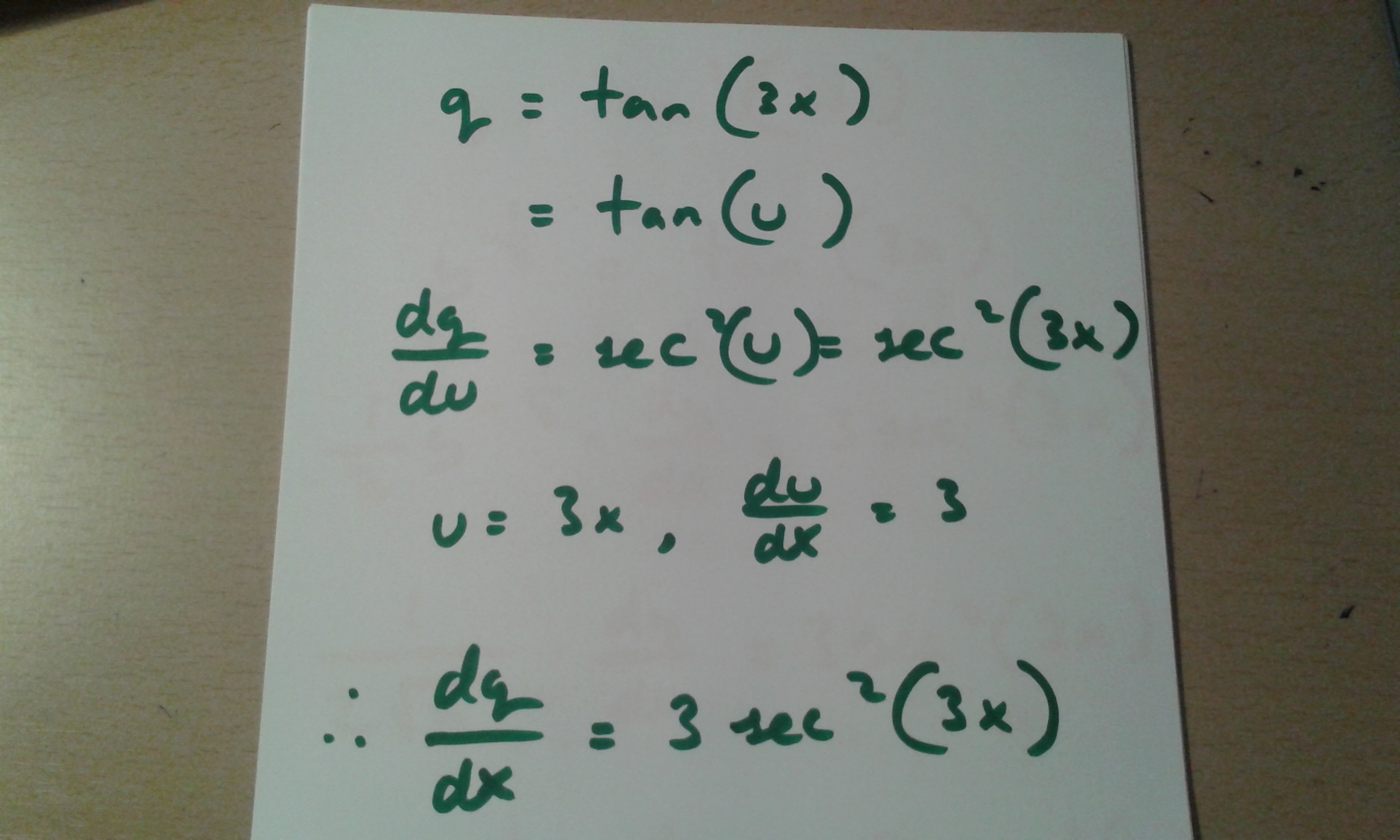



How Do You Find The Derivative Of Tan 2 3x Socratic




A Differentiate The Following Function With Respect Chegg Com
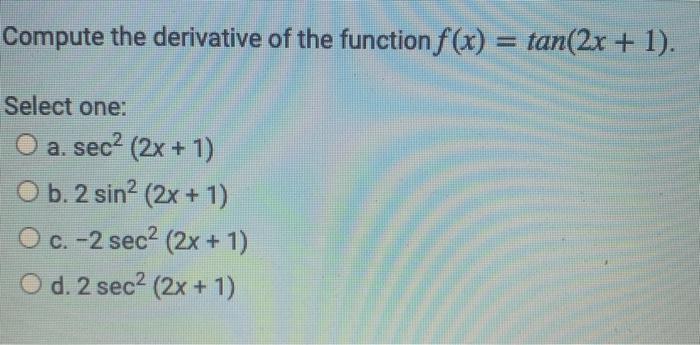



Compute The Derivative Of The Function F X Tan 2x Chegg Com




06 Derivative By Substitution Of Trigonometric Ratio Tan 2 X 3 2tans Tan2x Youtube




Ap Calculus Ab How Do I Find The Derivative Of The Trig Function Of A Trig Function Y Sin Tan2x Homeworkhelp
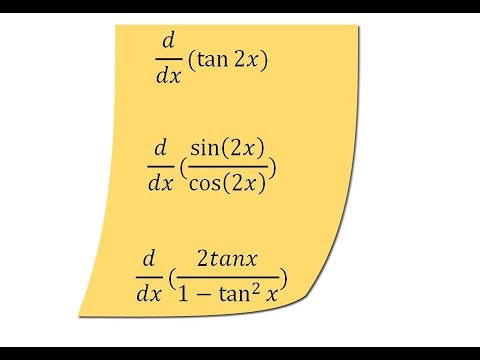



Derivative Of Tan2x Sin2x Cos2x And 2tanx 1 Tan 2x Youtube




Find The Range Of F X Sqrt 4 Sqrt 1 Tan 2x
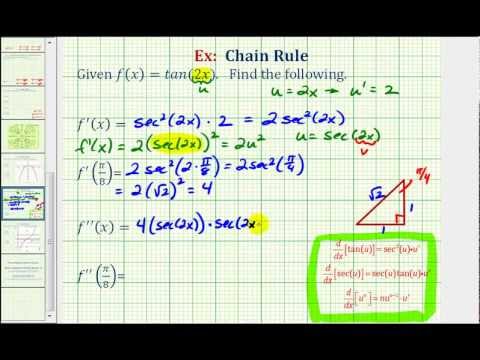



Ex 1 First And Second Derivatives Using The Chain Rule F X Tan 2x Youtube




Derivative Of Tan Inverse With Chain Rule Youtube




The Derivative Of H X 2 Sec 2 X Tan X Product Rule Example Youtube




Question 4 Find The Derivative Of F X 2x Sec2x O Chegg Com




Differentiate Tanx Tan 2x Tan 3x Tan 4x W R T X Youtube




Maclaurin Series Tan X
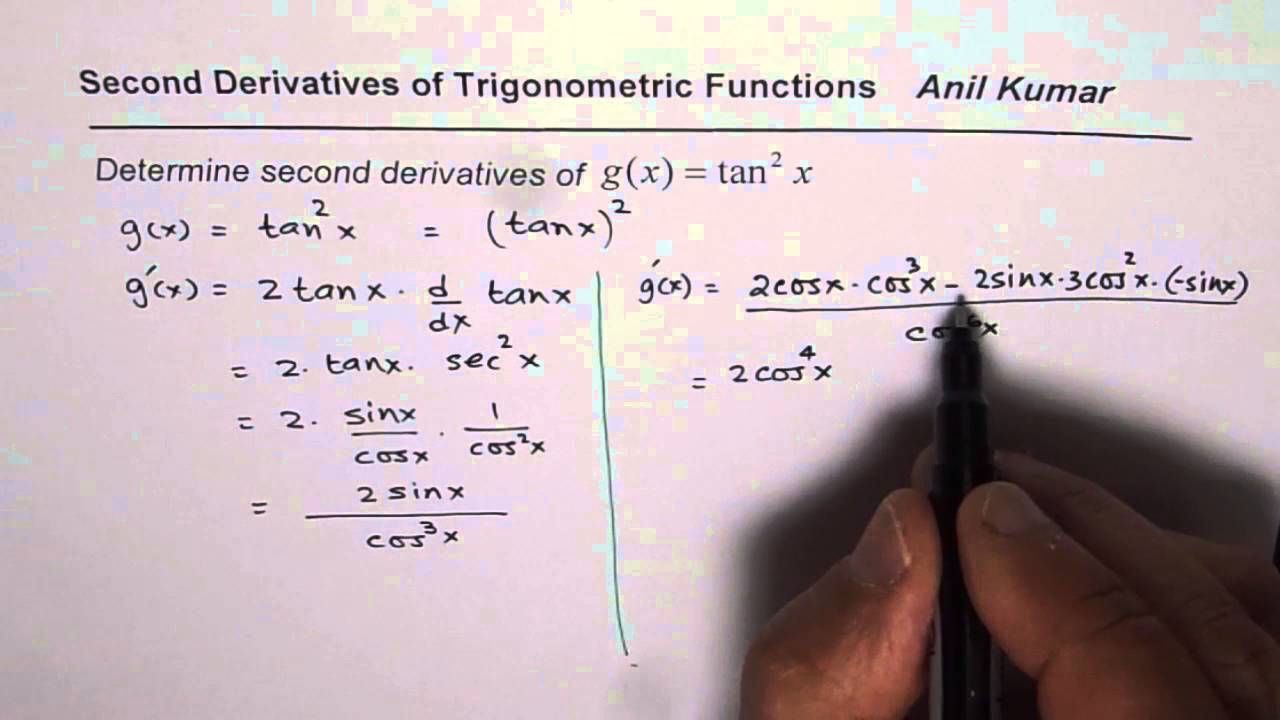



Second Derivative Of Tan 2x Youtube




Derivative Of Tan X Sec X Tan X More
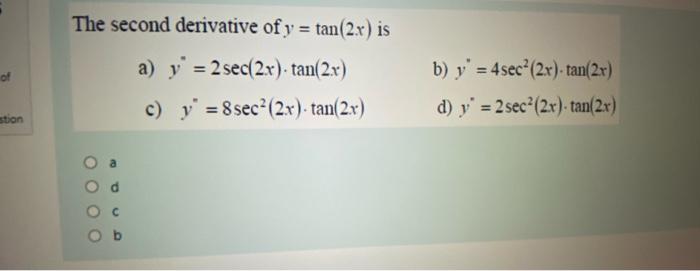



The Second Derivative Of Y Tan 2 X Is Of A Y 2 Chegg Com
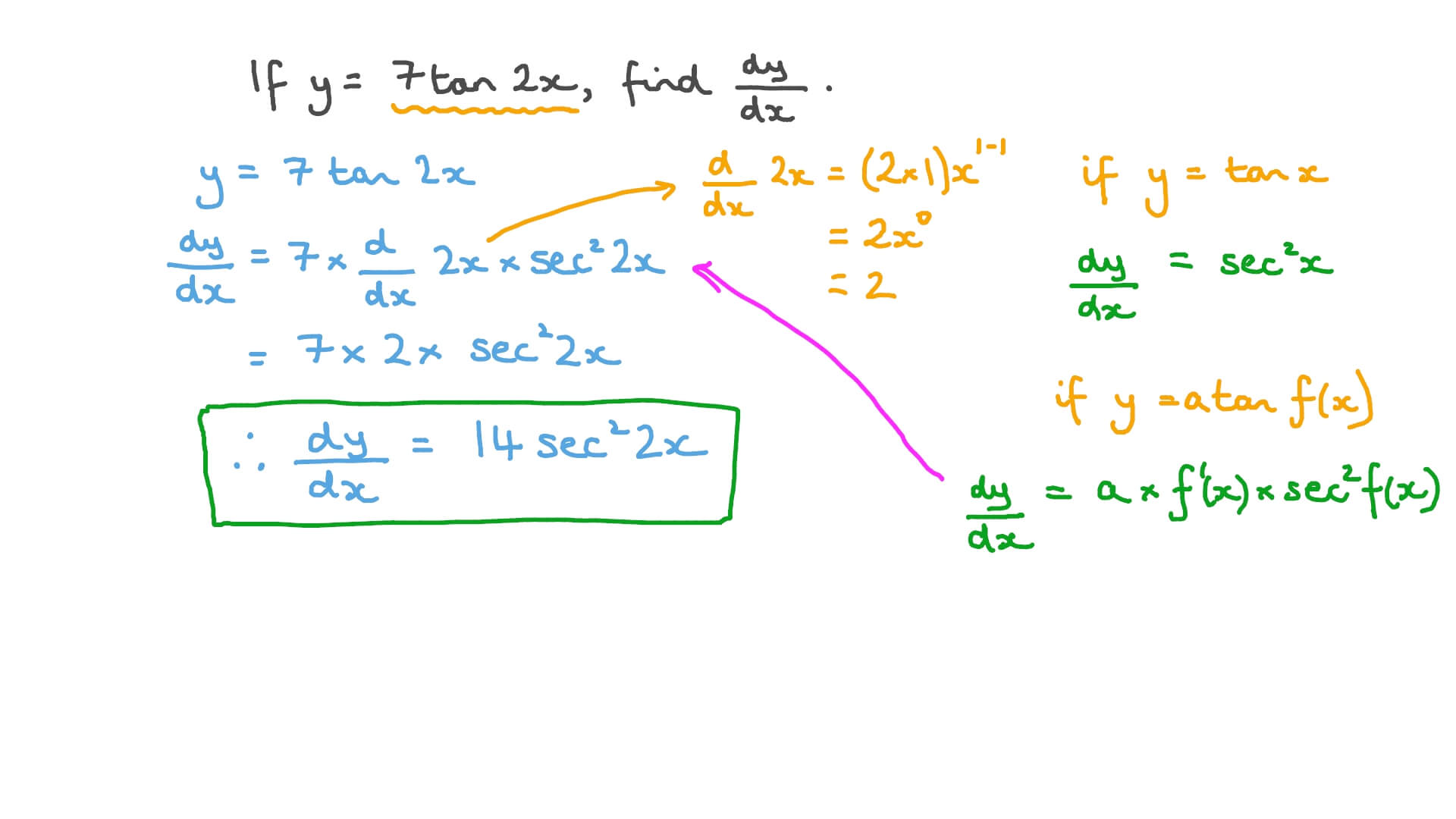



Question Video Differentiating Trigonometric Functions Nagwa




Derivative Of Arctan X Inverse Tangent Detailed Lesson




1 Find The Derivative Of Each Function A E E 7 Chegg Com
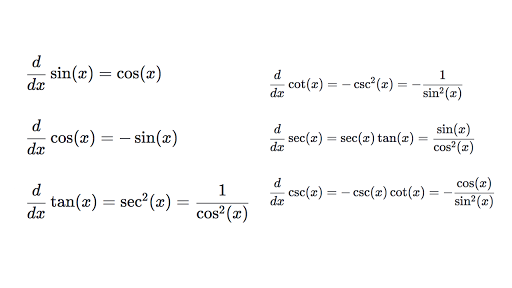



Differentiating Trigonometric Functions Review Article Khan Academy




The Derivative Of Tan 2x W R T Cos 2x Is Maths Limits And Derivatives Meritnation Com




Lim X 0 Log Tan 2x Tan 2 2x
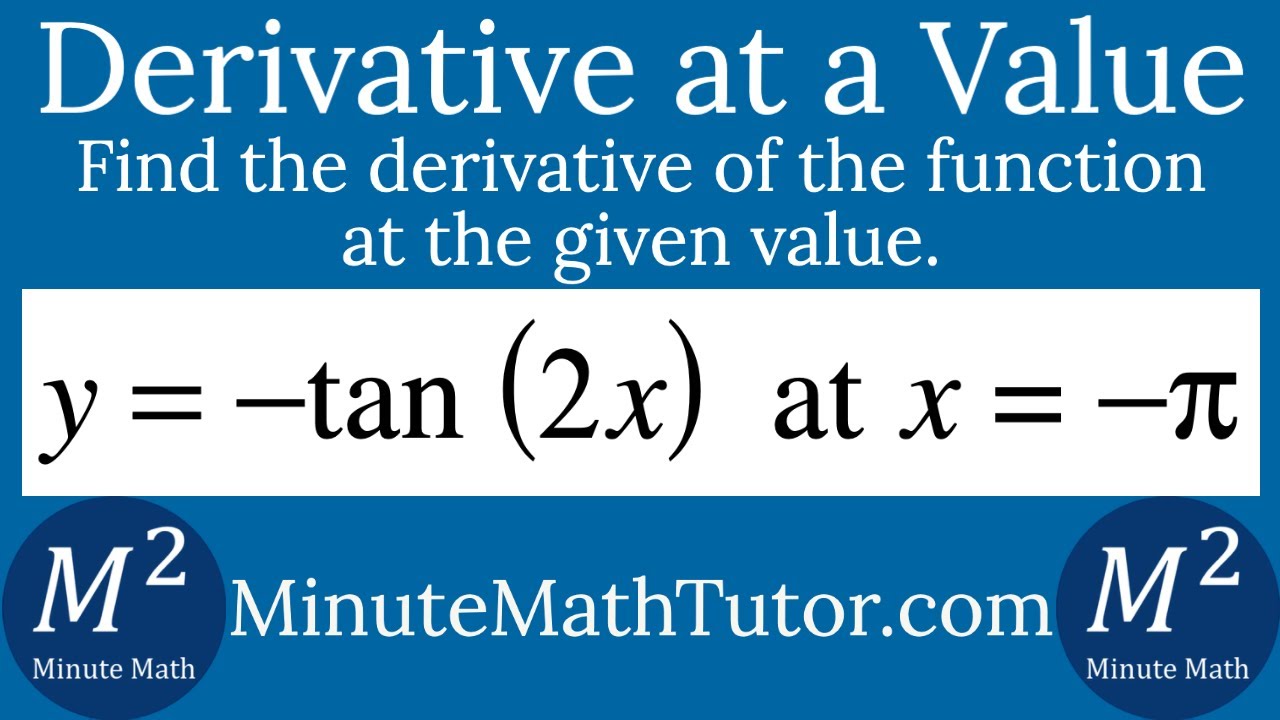



Find The Derivative Of Y Tan 2x At X P Youtube




Derivative Of Tan 2x 3 Is A 2sec 2x 3 B Sec 2x 3 C Sec 2x 3 D None Of These Snapsolve
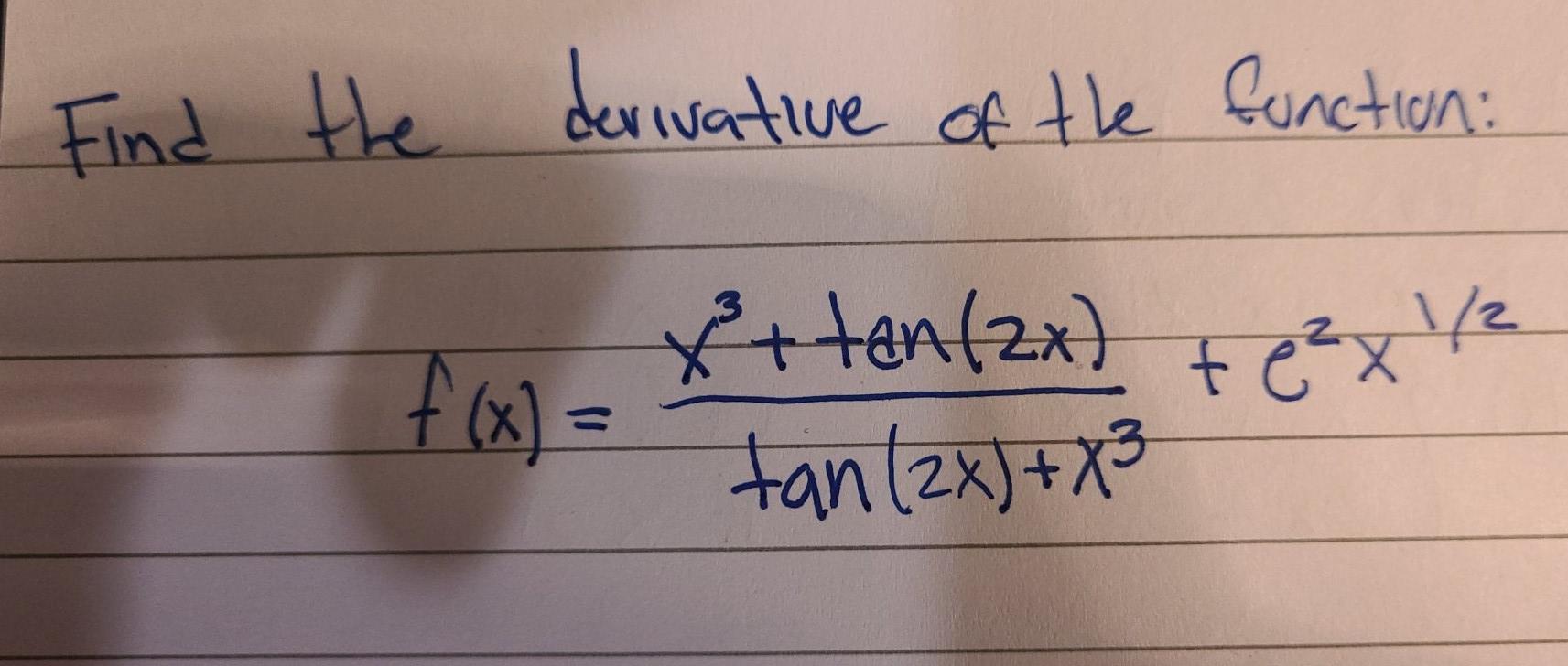



Find The Derivative Of The Function X Tan 2x X Chegg Com




Find The Derivative Of The Following Functions 1 Gauthmath




Differentiate The Following From First Principle Tan 2x




How To Take The Derivative Of Tan X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Derivative Of Arctan X Inverse Tangent Detailed Lesson



Derivative Of Inverse Tangent
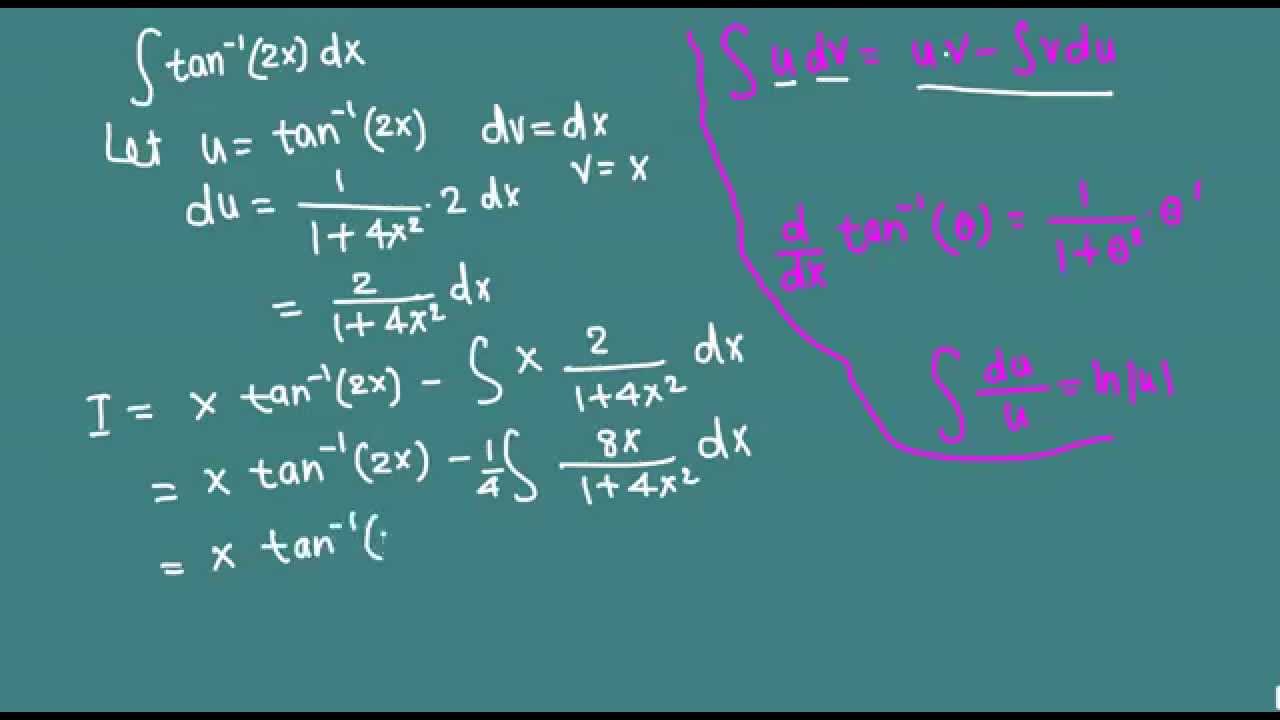



Integration Of Inverse Tan 2x Integration By Parts Youtube



1



What Is The Nth Derivative Of Tan 1 2x 1 X 2 Quora




Brandi S Buzzar Blog Proof Derivative Tan X Sec 2 X




Derivative Of Tan 2x




Derivative Of Tan X Sec X Tan X More
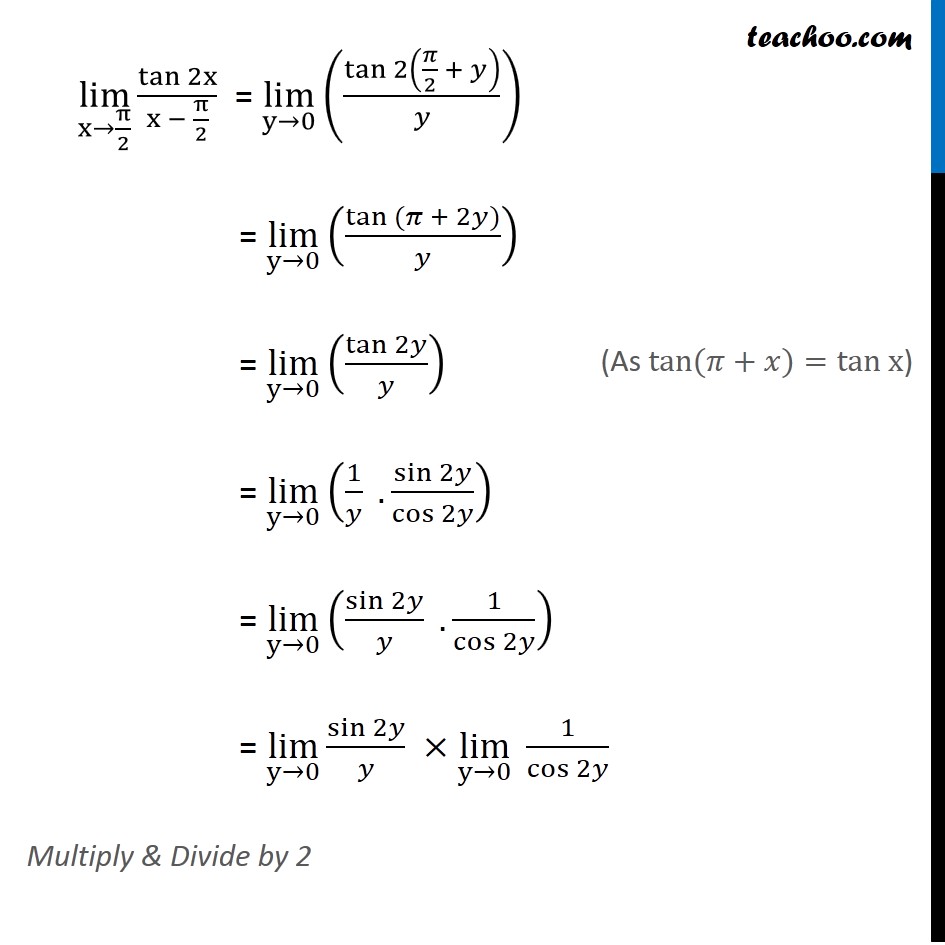



Ex 13 1 22 Lim X Pi 2 Tan 2x X Pi 2 Chapter 13 Class 11



Www Math Purdue Edu Kyochman Ma Lesson14 Notes Implicitdifferentiation Pdf




How To Calculate The Derivative Of Sec 2 X Quora




Differentiation With Trig Outcomes Ppt Download




Derivative Rules For Trigonometric Functions
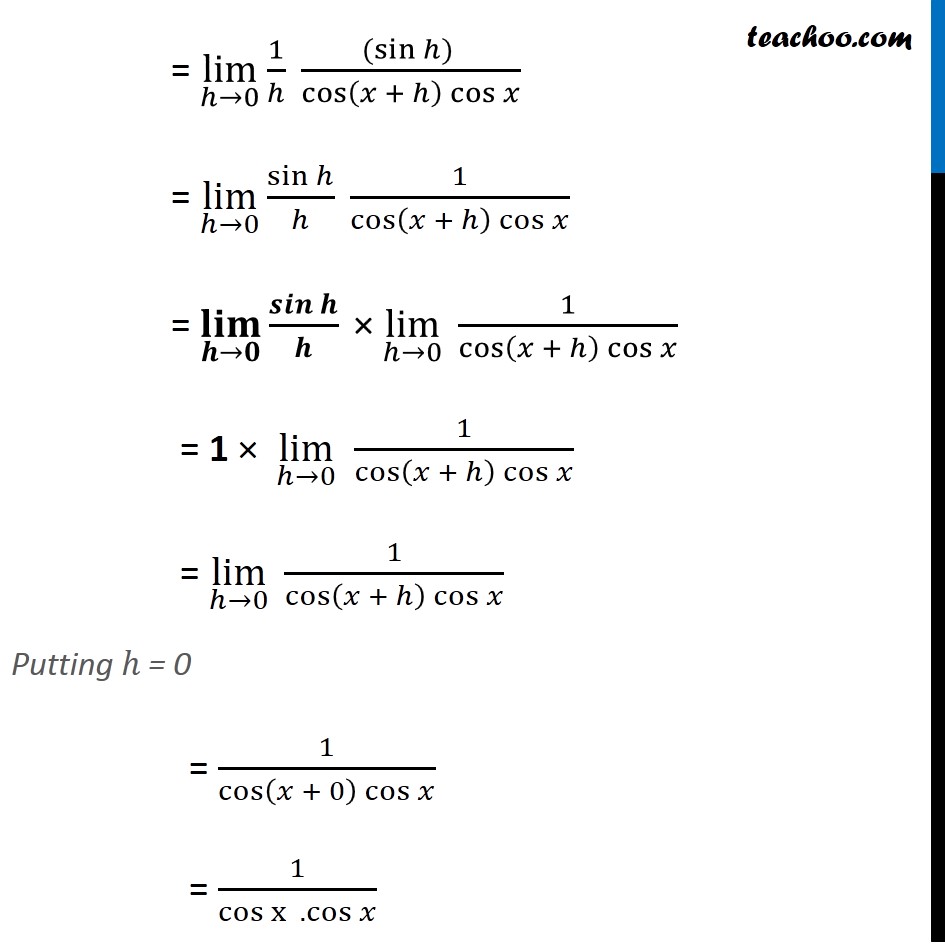



Prove That Derivative Of Tan X Is Sec 2 X By First Principle




Evaluate Limit X Tends To Pi 2 Tan 2x X Pi 2 Evaluate Sin X Sin A X A Maths Limits And Derivatives Meritnation Com




Derivative Of Tan 2x 3 From First Principle Brainly In



1




Tan2x ただの悪魔の画像
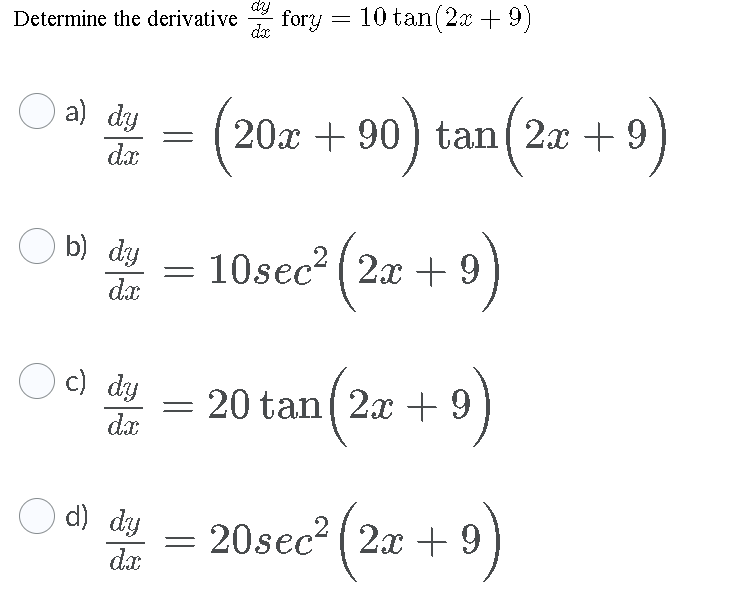



Determine The Derivative Fory 10 Tan 2x 9 O A Dy Chegg Com



1




Finding The Derivative Of Sec 2 X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



How Do I Integrate Tan 2 X Youtube



Derivatives Of The Trigonometric Functions




Which Of The Following Is The Derivative Of x Chegg Com




Find The Derivative Of The Given Function Y Tan 2x 1 Cot 2x I Tried Converting The Original Function In Terms Of Sin And Cos But It Was Still Too Complicated To Be Called Simplified




The Derivative Of Tan 2x Derivativeit




Ii 1 Find The Derivatives Of The Following Functions From The First Principles X3 I X4 4 Iii Ax Bx C Iv Vx 1 V Sin 2x Vi Cos




Derivative Of Tan X Sec X Tan X More




2 Use The Chain Rule To Find The Derivative Of Chegg Com



Differentiate The Following From First Principles I Tan 2 X Ii Tan 2x 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



What Is The Derivative Of Tan X 45 Quora



Solved Find The Derivative Using Inverse Trigonometric Functions And Simplify Further If Possible Course Hero



Find The Derivative Of Fx Sec Tan 2x Gauthmath




Clicker Question 1 What Is The Derivative Of F X 7x 4 E X Sin X A 28x 3 E X Cos X B 28x 3 E X Cos X




3 Determine The First Derivative Of The Following Gauthmath



What Is D Dx Tan2x Quora



Derivatives Of Inverse Trigonometric Functions Sin 1 2x Cos 1 X 2 Tan 1 X 2 Sec 1 1 X 2 Youtube




How To Take The Derivative Of Tan X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
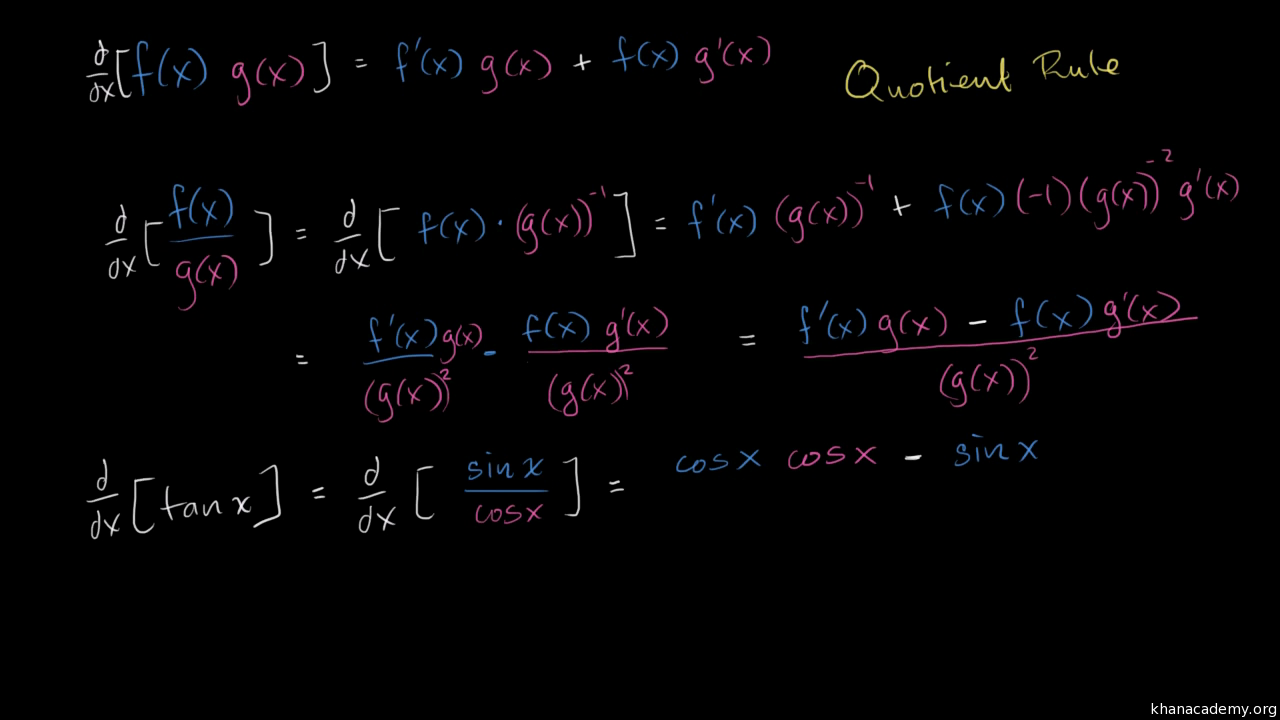



Derivative Of Tan X Old Video Khan Academy
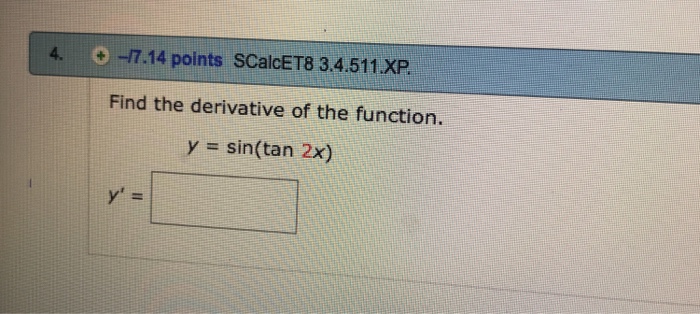



Find The Derivative Of The Function Y Sin Tan 2x Chegg Com




Find The Second Derivative Of The Function Y Tan 2x Chegg Com




05 Derivative Of Tangent Function Tan2x And Tanx 2 Youtube
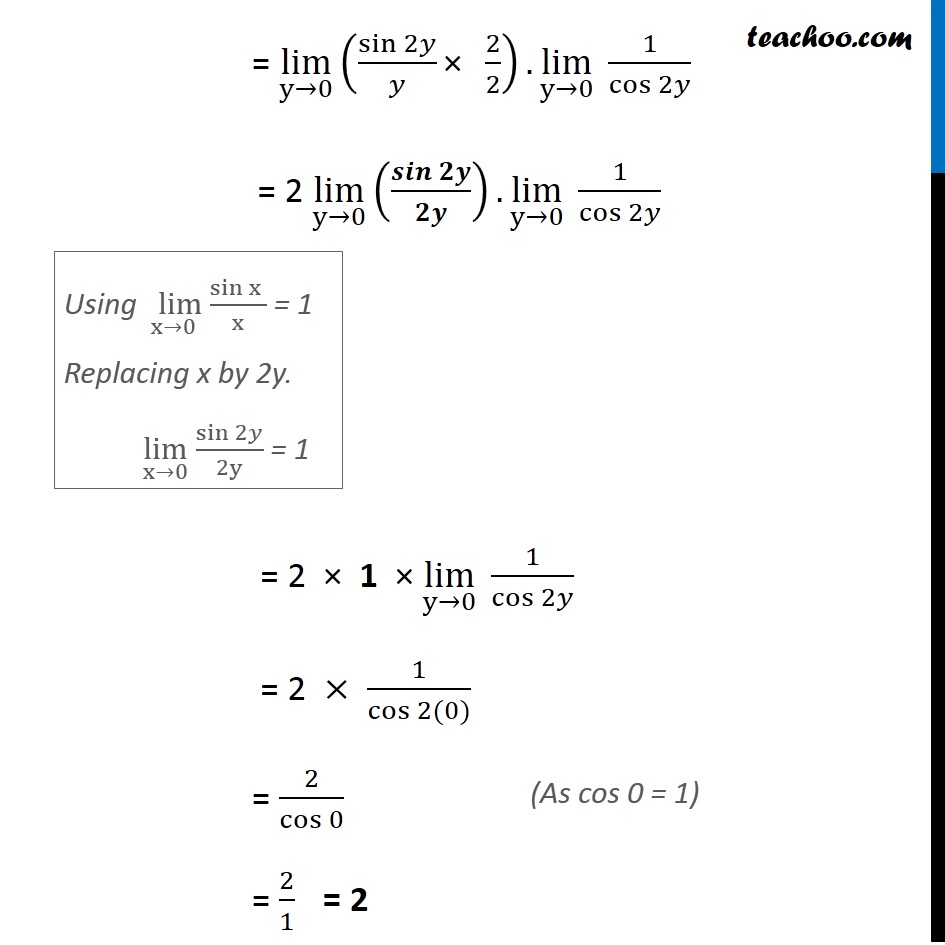



Ex 13 1 22 Lim X Pi 2 Tan 2x X Pi 2 Chapter 13 Class 11
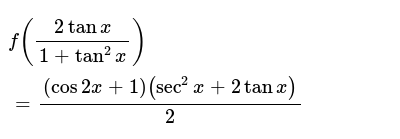



F 2tanx 1 Tan 2x Cos2x 1 Sec 2x 2tanx 2
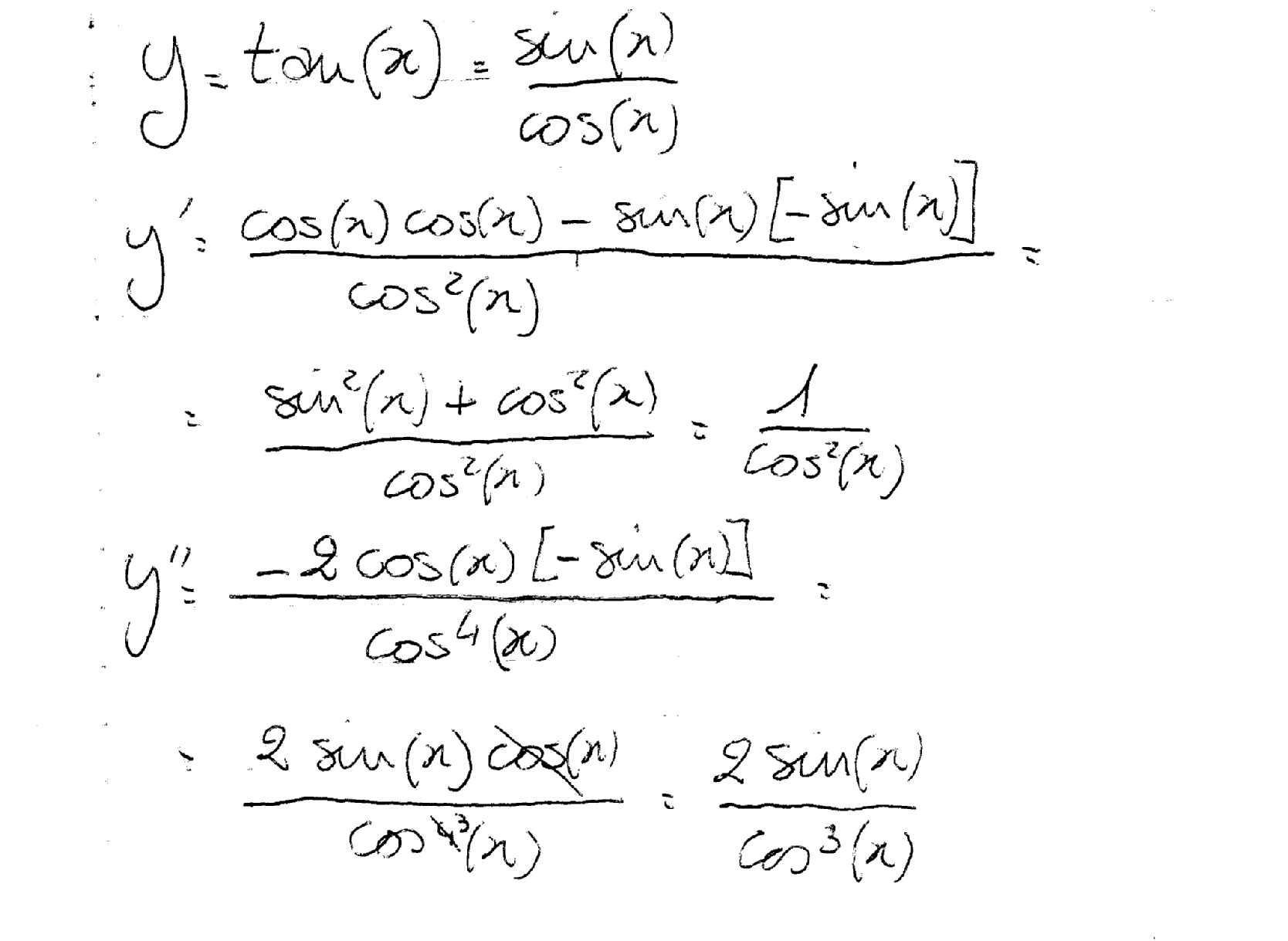



What Is The 2nd Derivative Of Y Tanx Socratic



Derivatives Of Trigonometric Functions



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿